No-See-Ums or also known as biting midges can be a total nuisance to fisherman, campers, hunters, hikers, gardeners, and others who spend time outdoors during early morning and evenings, and even during the daytime on cloudy days when winds are calm. They will readily bite humans; the bites are irritating, painful, and can cause long-lasting painful lesions for some people.
If bitten by this insect, people will tend to feel the bite, but they cannot see what it is. Hence, why it is called No-See-Ums. These biting midges are incorrectly referred to as sand flies sometimes.
Species
There are 4,000+ species of biting midges in the Ceratopogonidae family. Species belonging to the genus Leptoconops occur in the tropics, sub-tropics, the Caribbean/
The Leptoconops torrens or no-see-ums belong to the Ceratopogonidae family. They are about 1/16-inch long. No-see-ums slip under loose clothing to get a blood meal.
Appearance
They are gray in color and are less than 1/8-inch long with two wings. These wing patterns are used by biologists to identify species. No-see-ums have large compound eyes and a 15-segmented antennae. Their mouthparts have cutting teeth with elongated mandibles adapted for blood-sucking only in females.
Life Cycle
Adults: They progress from egg to larva to pupa, and then to adult stage. This cycle occurs in two to six weeks.
Mating occurs while the male and female are in flight when females fly into swarms of males. Some of the species mate without swarming. Mating occurs when she finishes feeding.
Eggs: Males and females usually feed on nectar. Females require blood from hosts for their eggs to mature. Blood meals are required for batches of eggs. This life cycle takes about two years from egg to adult.
Like mosquitoes, only the female no-see-ums bite. The insects breed when the weather warms in the spring, usually in May and June, and they remain a pest for several weeks/ They need a blood meal to complete their reproductive cycle.
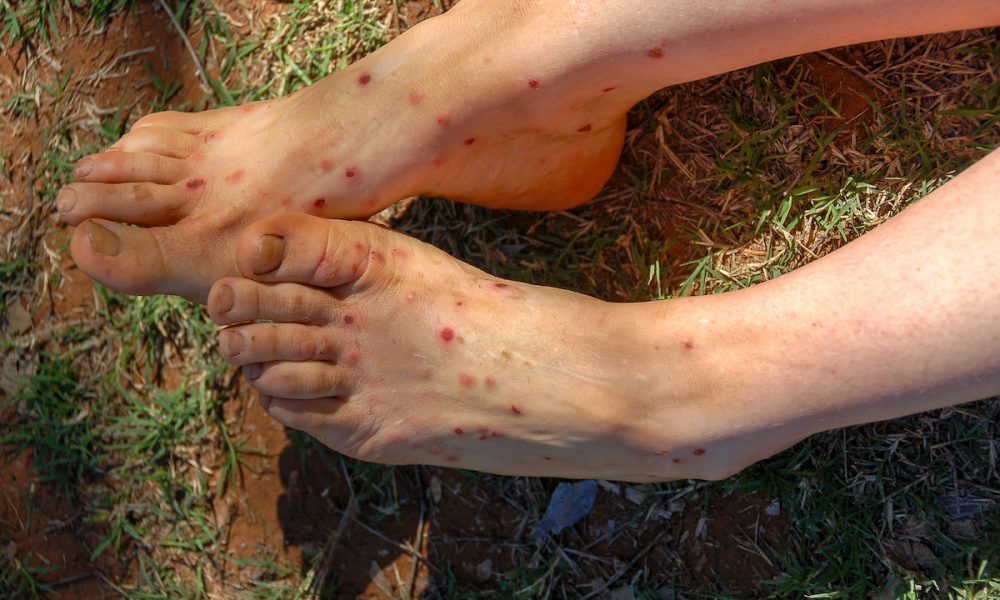
Bites
They bite domestic and wild animals and birds. The females inject saliva into the skin, which pools the blood just beneath the surface, resulting in a small red dot that becomes excruciatingly itchy. A single bite can welt into a one-or two-inch diameter spot, which lasts about two weeks.
People should not scratch the welts, as scratching makes the itchy bites last twice as long and can lead to infected sores.
To avoid being bitten, limit exposure by not sitting long in places where they are likely to occur, or where you’ve heard of problem areas. Move quickly through the area.
Contact Us
Choose Proactive Pest Control for professional, comprehensive, guaranteed pest, and lawn management. The pros at Proactive will work diligently to gain your trust, confidence, and your total satisfaction. CALL US TODAY at 770-800-PEST to schedule a free, no obligation inspection and evaluation for your home or business. Or, contact us for a FREE consultation. Let us show you why Proactive Pest Control is northeast Georgia’s first choice for pest, termite, and lawn services.